Remove Stinger Program
FIM 9. 2 Stinger Wikipedia. Stinger. A U. S. Marine with a field radio relays the direction of aircraft approaching to the operator of an FIM 9. McAfee Stinger is a portable and free application designed to remove malwareinfected files from the computer. It scans the hard disk on demand and detects. McAfee Stinger is a standalone utility used to detect and remove specific viruses. It is not a substitute for full antivirus protection, but a specialized tool to. Bluenote Stinger Burnto Suting is the former Deputy Commander of Grimoire. Directx 10 For Windows Vista Ultimate more. Remove Stinger Program' title='Remove Stinger Program' />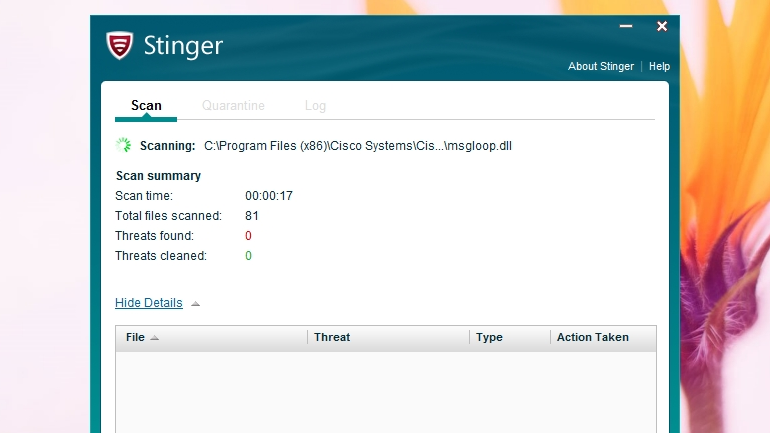 Stinger missile launcher in September 1. Type. Man portable surface to air missile. Place of origin. United States. Download-McAfee-Stinger-Portable-12.1.jpg' alt='Remove Stinger Program' title='Remove Stinger Program' />
Stinger missile launcher in September 1. Type. Man portable surface to air missile. Place of origin. United States. Download-McAfee-Stinger-Portable-12.1.jpg' alt='Remove Stinger Program' title='Remove Stinger Program' /> Service history. In service. Used by. See Operators. Wars. Falklands War, SovietAfghan War, Angolan Civil War, Sri Lankan Civil War, ChadianLibyan conflict, Tajikistani Civil War, Kargil War, Yugoslav Wars, Invasion of Grenada, Second Chechen War, Syrian Civil War, Iraqi Civil War 2. Production history. Designer. General Dynamics. Designed. 19. 67. Manufacturer. Raytheon Missile Systems. Unit cost. U. S. 3. Produced. 19. 78present. Variants. FIM 9. A, FIM 9. B, FIM 9. C, FIM 9. D, FIM 9. GSpecifications FIM 9. StingerWeight. 33. Length. 59. 8 in 1. Diameter. 2. 7. 6 in 7. Crew. 1Effective firing range. Dell Drivers Dhm Download. FIM 9. 2C Stinger RMP1Warhead. High explosive Annular blast fragmentation. Warhead weight. 3 kg 6. Engine. Solid fuel rocket motor. Pokemon Emerald Gameshark Action Replay. Guidancesystem. Infrared homing. Launchplatform. MANPADS, M6 Linebacker, Eurocopter Tiger, ANTWQ 1 Avenger, MQ 1 Predator, AH 6. Apache, T 1. 29 ATAKThe FIM 9. Stinger is a Man Portable Air Defense System MANPADS that operates as an infrared homingsurface to air missile SAM. It can be adapted to fire from a wide variety of ground vehicles and helicopters as an AAM. Developed in the United States this weapon system entered service in 1. United States and by 2. It is principally manufactured by Raytheon Missile Systems and is produced under license by EADS in Germany and by Roketsan in Turkey with 7. DescriptioneditLight to carry and easy to operate, the FIM 9. Stinger is a passive surface to air missile, that can be shoulder fired by a single operator although standard military procedure calls for two operators, spotter and gunner. The FIM 9. 2B missile can also be fired from the M 1. Avenger and the M6 Linebacker. The missile is also capable of being deployed from a Humvee Stinger rack, and can be used by airborne troops. A helicopter launched version exists called Air to Air Stinger ATAS. The missile is 5. The missile itself weighs 2. The Stinger is launched by a small ejection motor that pushes it a safe distance from the operator before engaging the main two stage solid fuel sustainer, which accelerates it to a maximum speed of Mach 2. The warhead is a 3 kg penetrating hit to kill warhead type with an impact fuze and a self destruct timer. To fire the missile, a BCU Battery Coolant Unit is inserted into the handguard. This shoots a stream of argon gas into the system, as well as a chemical energy charge that enables the acquisition indicators and missile to get power. The batteries are somewhat sensitive to abuse, with a limited amount of gas. Over time, and without proper maintenance, they can become unserviceable. The IFF system receives power from a rechargeable battery. Guidance to the target is initially through proportional navigation, then switches to another mode that directs the missile towards the target airframe instead of its exhaust plume. There are three main variants in use the Stinger basic, STINGER Passive Optical Seeker Technique POST, and STINGER Reprogrammable Microprocessor RMP. These correspond to the FIM 9. A, FIM 9. 2B, and FIM 9. C and later variants respectively. The POST has a dual detector seeker IR and UV. This allows it to distinguish targets from countermeasures much better than the Redeye and FIM 9. A, which have IR only. While modern flares can have an IR signature that is closely matched to the launching aircrafts engine exhaust, there is a readily distinguishable difference in UV signature between flares and jet engines. The Stinger RMP is so called because of its ability to load a new set of software via ROM chip inserted in the grip at the depot. If this download to the missile fails during power up, basic functionality runs off the on board ROM. The four processor RMP has 4 KB of RAM for each processor. Since the downloaded code runs from RAM, there is little space to spare, particularly for processors dedicated to seeker input processing and target analysis. Historyedit. A U. S. Marine fires an FIM 9. A Stinger missile during a July 2. California. Initial work on the missile was begun by General Dynamics in 1. FM 4. 3 Redeye II. Production of the Redeye II ran from 1. It was accepted for further development by the U. S. Army in 1. 97. FIM 9. 2 the Stinger appellation was chosen in 1. Because of technical difficulties that dogged testing, the first shoulder launch was not until mid 1. Production of the FIM 9. A began in 1. 97. FIM 4. 3 Redeye. An improved Stinger with a new seeker, the FIM 9. B, was produced from 1. FIM 9. 2A. Production of both the A and B types ended in 1. The replacement FIM 9. C had been developed from 1. The first examples were delivered to front line units in 1. C type missiles were fitted with a reprogrammable electronics system to allow for upgrades. The missiles which received a counter measures upgrade were designated D and later upgrades to the D were designated G. The FIM 9. 2E or Block I was developed from 1. FIM 9. 2D is also part of the Block I development. The main changes were again in the sensor and the software, improving the missiles performance against smaller and low signature targets. A software upgrade in 2. F. Block II development began in 1. Production was scheduled for 2. Janes reports that this may be on hold. Since 1. 98. 4 the Stinger has been issued to many U. S. Navywarships for point defense, particularly in Middle Eastern waters, with a three man team that can perform other duties when not conducting Stinger training or maintenance. Until it was decommissioned in September 1. U. S. Navy had at least one Stinger Gunnery Detachment attached to Beachmaster Unit Two in Little Creek Virginia. The sailors of this detachment would deploy to carrier battlegroups in teams of two to four sailors per ship as requested by Battle Group Commanders. VariantseditFIM 9. A, Stinger Basic The basic model. FIM 9. B, Stinger POST In this version, the infrared seeker head was replaced by a combined IRUV seeker that utilized rosette scanning. This resulted in achieving significantly higher resistance to enemy countermeasures flares and natural disturbances. Production ran from 1. FIM 9. 2C, Stinger RMP The resistance to interference was increased again by adding more powerful digital computer components. Moreover, the software of the missile could now be reconfigured in a short time in order to respond quickly and efficiently to new types of countermeasures. Until 1. 99. 1, some 2. U. S. Army alone. FIM 9. D Various modifications were continued with this version in order to increase the resistance to interference. FIM 9. E Stinger RMP Block I By adding a new rollover sensor and revised control software, the flight behavior was significantly improved. Additionally, the performance against small targets such as drones, cruise missiles and light reconnaissance helicopters was improved. The first deliveries began in 1. Almost the entire stock of U. S. Stinger missiles was replaced by this version. FIM 9. F A further improvement of the E version and the current production version. FIM 9. G An unspecified upgrade for the D variant. FIM 9. H Indicates a D variant that has been upgraded to the E standard.
Service history. In service. Used by. See Operators. Wars. Falklands War, SovietAfghan War, Angolan Civil War, Sri Lankan Civil War, ChadianLibyan conflict, Tajikistani Civil War, Kargil War, Yugoslav Wars, Invasion of Grenada, Second Chechen War, Syrian Civil War, Iraqi Civil War 2. Production history. Designer. General Dynamics. Designed. 19. 67. Manufacturer. Raytheon Missile Systems. Unit cost. U. S. 3. Produced. 19. 78present. Variants. FIM 9. A, FIM 9. B, FIM 9. C, FIM 9. D, FIM 9. GSpecifications FIM 9. StingerWeight. 33. Length. 59. 8 in 1. Diameter. 2. 7. 6 in 7. Crew. 1Effective firing range. Dell Drivers Dhm Download. FIM 9. 2C Stinger RMP1Warhead. High explosive Annular blast fragmentation. Warhead weight. 3 kg 6. Engine. Solid fuel rocket motor. Pokemon Emerald Gameshark Action Replay. Guidancesystem. Infrared homing. Launchplatform. MANPADS, M6 Linebacker, Eurocopter Tiger, ANTWQ 1 Avenger, MQ 1 Predator, AH 6. Apache, T 1. 29 ATAKThe FIM 9. Stinger is a Man Portable Air Defense System MANPADS that operates as an infrared homingsurface to air missile SAM. It can be adapted to fire from a wide variety of ground vehicles and helicopters as an AAM. Developed in the United States this weapon system entered service in 1. United States and by 2. It is principally manufactured by Raytheon Missile Systems and is produced under license by EADS in Germany and by Roketsan in Turkey with 7. DescriptioneditLight to carry and easy to operate, the FIM 9. Stinger is a passive surface to air missile, that can be shoulder fired by a single operator although standard military procedure calls for two operators, spotter and gunner. The FIM 9. 2B missile can also be fired from the M 1. Avenger and the M6 Linebacker. The missile is also capable of being deployed from a Humvee Stinger rack, and can be used by airborne troops. A helicopter launched version exists called Air to Air Stinger ATAS. The missile is 5. The missile itself weighs 2. The Stinger is launched by a small ejection motor that pushes it a safe distance from the operator before engaging the main two stage solid fuel sustainer, which accelerates it to a maximum speed of Mach 2. The warhead is a 3 kg penetrating hit to kill warhead type with an impact fuze and a self destruct timer. To fire the missile, a BCU Battery Coolant Unit is inserted into the handguard. This shoots a stream of argon gas into the system, as well as a chemical energy charge that enables the acquisition indicators and missile to get power. The batteries are somewhat sensitive to abuse, with a limited amount of gas. Over time, and without proper maintenance, they can become unserviceable. The IFF system receives power from a rechargeable battery. Guidance to the target is initially through proportional navigation, then switches to another mode that directs the missile towards the target airframe instead of its exhaust plume. There are three main variants in use the Stinger basic, STINGER Passive Optical Seeker Technique POST, and STINGER Reprogrammable Microprocessor RMP. These correspond to the FIM 9. A, FIM 9. 2B, and FIM 9. C and later variants respectively. The POST has a dual detector seeker IR and UV. This allows it to distinguish targets from countermeasures much better than the Redeye and FIM 9. A, which have IR only. While modern flares can have an IR signature that is closely matched to the launching aircrafts engine exhaust, there is a readily distinguishable difference in UV signature between flares and jet engines. The Stinger RMP is so called because of its ability to load a new set of software via ROM chip inserted in the grip at the depot. If this download to the missile fails during power up, basic functionality runs off the on board ROM. The four processor RMP has 4 KB of RAM for each processor. Since the downloaded code runs from RAM, there is little space to spare, particularly for processors dedicated to seeker input processing and target analysis. Historyedit. A U. S. Marine fires an FIM 9. A Stinger missile during a July 2. California. Initial work on the missile was begun by General Dynamics in 1. FM 4. 3 Redeye II. Production of the Redeye II ran from 1. It was accepted for further development by the U. S. Army in 1. 97. FIM 9. 2 the Stinger appellation was chosen in 1. Because of technical difficulties that dogged testing, the first shoulder launch was not until mid 1. Production of the FIM 9. A began in 1. 97. FIM 4. 3 Redeye. An improved Stinger with a new seeker, the FIM 9. B, was produced from 1. FIM 9. 2A. Production of both the A and B types ended in 1. The replacement FIM 9. C had been developed from 1. The first examples were delivered to front line units in 1. C type missiles were fitted with a reprogrammable electronics system to allow for upgrades. The missiles which received a counter measures upgrade were designated D and later upgrades to the D were designated G. The FIM 9. 2E or Block I was developed from 1. FIM 9. 2D is also part of the Block I development. The main changes were again in the sensor and the software, improving the missiles performance against smaller and low signature targets. A software upgrade in 2. F. Block II development began in 1. Production was scheduled for 2. Janes reports that this may be on hold. Since 1. 98. 4 the Stinger has been issued to many U. S. Navywarships for point defense, particularly in Middle Eastern waters, with a three man team that can perform other duties when not conducting Stinger training or maintenance. Until it was decommissioned in September 1. U. S. Navy had at least one Stinger Gunnery Detachment attached to Beachmaster Unit Two in Little Creek Virginia. The sailors of this detachment would deploy to carrier battlegroups in teams of two to four sailors per ship as requested by Battle Group Commanders. VariantseditFIM 9. A, Stinger Basic The basic model. FIM 9. B, Stinger POST In this version, the infrared seeker head was replaced by a combined IRUV seeker that utilized rosette scanning. This resulted in achieving significantly higher resistance to enemy countermeasures flares and natural disturbances. Production ran from 1. FIM 9. 2C, Stinger RMP The resistance to interference was increased again by adding more powerful digital computer components. Moreover, the software of the missile could now be reconfigured in a short time in order to respond quickly and efficiently to new types of countermeasures. Until 1. 99. 1, some 2. U. S. Army alone. FIM 9. D Various modifications were continued with this version in order to increase the resistance to interference. FIM 9. E Stinger RMP Block I By adding a new rollover sensor and revised control software, the flight behavior was significantly improved. Additionally, the performance against small targets such as drones, cruise missiles and light reconnaissance helicopters was improved. The first deliveries began in 1. Almost the entire stock of U. S. Stinger missiles was replaced by this version. FIM 9. F A further improvement of the E version and the current production version. FIM 9. G An unspecified upgrade for the D variant. FIM 9. H Indicates a D variant that has been upgraded to the E standard.